浅谈iOS之weak底层实现原理
在iOS开发过程中,会经常使用到一个修饰词“weak”,使用场景大家都比较清晰,用于一些对象相互引用的时候,避免出现强强引用,对象不能被释放,出现内存泄露的问题。
weak 关键字的作用弱引用,所引用对象的计数器不会加一,并在引用对象被释放的时候自动被设置为 nil。
weak底层原理
1.weak编译解析
首先需要看一下weak编译之后具体出现什么样的变化,通过Clang的方法把weak编译成C++
int main(){
NSObject *obj = [[NSObject alloc] init];
id __weak obj1 = obj;
}
编译之后的weak,通过objc_ownership(weak)实现weak方法,objc_ownership字面意思是:获得对象的所有权,是对对象weak的初始化的一个操作。
在使用clang编译过程中会报错误,使用下方的方法编码编译出现error clang -rewrite-objc -fobjc-arc -stdlib=libc++ -mmacosx-version-min=10.7 -fobjc-runtime=macosx-10.7 -Wno-deprecated-declarations main.m
int main(){
NSObject *obj = ((NSObject *(*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)((NSObject *(*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)objc_getClass("NSObject"), sel_registerName("alloc")), sel_registerName("init"));
id __attribute__((objc_ownership(weak))) obj1 = obj;
}
2.weak的实现原理
第一、通过weak编译解析,可以看出来weak通过runtime初始化的并维护的;
第二、weak和strong都是Object-C的修饰词,而strong是通过runtime维护的一个自动计数表结构。
综上:weak是有Runtime维护的weak表。
在runtime源码中,可以找到'objc-weak.h'和‘objc-weak.mm’文件,并且在objc-weak.h文件中关于定义weak表的结构体以及相关的方法。
2.1.weak表 weak_table_t是一个全局weak 引用的表,使用不定类型对象的地址作为 key,用 weak_entry_t 类型结构体对象作为 value 。其中的 weak_entries 成员
/**
* The global weak references table. Stores object ids as keys,
* and weak_entry_t structs as their values.
*/
struct weak_table_t {
weak_entry_t *weak_entries; //保存了所有指向指定对象的weak指针 weak_entries的对象
size_t num_entries; // weak对象的存储空间
uintptr_t mask; //参与判断引用计数辅助量
uintptr_t max_hash_displacement; //hash key 最大偏移值
};
weak全局表中的存储weak定义的对象的表结构weak_entry_t,weak_entry_t是存储在弱引用表中的一个内部结构体,它负责维护和存储指向一个对象的所有弱引用hash表。其定义如下:
typedef objc_object ** weak_referrer_t;
struct weak_entry_t {
DisguisedPtr<objc_object> referent; //范型
union {
struct {
weak_referrer_t *referrers;
uintptr_t out_of_line : 1;
uintptr_t num_refs : PTR_MINUS_1;
uintptr_t mask;
uintptr_t max_hash_displacement;
};
struct {
// out_of_line=0 is LSB of one of these (don't care which)
weak_referrer_t inline_referrers[WEAK_INLINE_COUNT];
};
}
}
在 weak_entry_t 的结构中,DisguisedPtr referent 是对泛型对象的指针做了一个封装,通过这个泛型类来解决内存泄漏的问题。从注释中写 out_of_line 成员为最低有效位,当其为0的时候, weak_referrer_t 成员将扩展为多行静态 hash table。其实其中的 weak_referrer_t 是二维 objc_object 的别名,通过一个二维指针地址偏移,用下标作为 hash 的 key,做成了一个弱引用散列。
out_of_line:最低有效位,也是标志位。当标志位 0 时,增加引用表指针纬度。 num_refs:引用数值。这里记录弱引用表中引用有效数字,因为弱引用表使用的是静态 hash 结构,所以需要使用变量来记录数目。 mask:计数辅助量。 max_hash_displacement:hash 元素上限阀值。 其实 out_of_line 的值通常情况下是等于零的,所以弱引用表总是一个 objc_objective 指针二维数组。一维 objc_objective 指针可构成一张弱引用散列表,通过第三纬度实现了多张散列表,并且表数量为 WEAK_INLINE_COUNT 。
objc_object是weak_entry_t表中weak弱引用对象的范型对象的结构体结构。
struct objc_object {
private:
isa_t isa;
public:
// ISA() assumes this is NOT a tagged pointer object
Class ISA();
// getIsa() allows this to be a tagged pointer object
Class getIsa();
// initIsa() should be used to init the isa of new objects only.
// If this object already has an isa, use changeIsa() for correctness.
// initInstanceIsa(): objects with no custom RR/AWZ
// initClassIsa(): class objects
// initProtocolIsa(): protocol objects
// initIsa(): other objects
void initIsa(Class cls /*indexed=false*/);
void initClassIsa(Class cls /*indexed=maybe*/);
void initProtocolIsa(Class cls /*indexed=maybe*/);
void initInstanceIsa(Class cls, bool hasCxxDtor);
// changeIsa() should be used to change the isa of existing objects.
// If this is a new object, use initIsa() for performance.
Class changeIsa(Class newCls);
bool hasIndexedIsa();
bool isTaggedPointer();
bool isClass();
// object may have associated objects?
bool hasAssociatedObjects();
void setHasAssociatedObjects();
// object may be weakly referenced?
bool isWeaklyReferenced();
void setWeaklyReferenced_nolock();
// object may have -.cxx_destruct implementation?
bool hasCxxDtor();
// Optimized calls to retain/release methods
id retain();
void release();
id autorelease();
// Implementations of retain/release methods
id rootRetain();
bool rootRelease();
id rootAutorelease();
bool rootTryRetain();
bool rootReleaseShouldDealloc();
uintptr_t rootRetainCount();
// Implementation of dealloc methods
bool rootIsDeallocating();
void clearDeallocating();
void rootDealloc();
private:
void initIsa(Class newCls, bool indexed, bool hasCxxDtor);
// Slow paths for inline control
id rootAutorelease2();
bool overrelease_error();
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
// Unified retain count manipulation for nonpointer isa
id rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow);
bool rootRelease(bool performDealloc, bool handleUnderflow);
id rootRetain_overflow(bool tryRetain);
bool rootRelease_underflow(bool performDealloc);
void clearDeallocating_weak();
// Side table retain count overflow for nonpointer isa
void sidetable_lock();
void sidetable_unlock();
void sidetable_moveExtraRC_nolock(size_t extra_rc, bool isDeallocating, bool weaklyReferenced);
bool sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(size_t delta_rc);
bool sidetable_subExtraRC_nolock(size_t delta_rc);
size_t sidetable_getExtraRC_nolock();
#endif
// Side-table-only retain count
bool sidetable_isDeallocating();
void sidetable_clearDeallocating();
bool sidetable_isWeaklyReferenced();
void sidetable_setWeaklyReferenced_nolock();
id sidetable_retain();
id sidetable_retain_slow(SideTable *table);
bool sidetable_release(bool performDealloc = true);
bool sidetable_release_slow(SideTable *table, bool performDealloc = true);
bool sidetable_tryRetain();
uintptr_t sidetable_retainCount();
#if !NDEBUG
bool sidetable_present();
#endif
};
总之: 1.weak_table_t(weak 全局表):采用hash(哈希表)的方式把所有weak引用的对象,存储所有引用weak对象 2.weak_entry_t(weak_table_t表中hash表的value值,weak对象体):用于记录hash表中weak对象 3.objc_object(weak_entry_t对象中的范型对象,用于标记对象weak对象):用于标示weak引用的对象。
详细讲解weak存储对象结构,对接下来对weak操作使用可以更加清晰的理解weak的使用。
2.2.weak底层实现原理
在runtime源码中的NSObject.mm文件中找到了关于初始化和管理weak表的方法
- 初始化weak表方法
//初始化weak表
/**
* Initialize a fresh weak pointer to some object location.
* It would be used for code like:
*
* (The nil case)
* __weak id weakPtr;
* (The non-nil case)
* NSObject *o = ...;
* __weak id weakPtr = o;
*
* @param addr Address of __weak ptr.
* @param val Object ptr.
*/
id objc_initWeak(id *addr, id val)
{
*addr = 0;
if (!val) return nil;
return objc_storeWeak(addr, val); // 存储weak对象
}
- 存储weak对象的方法
/**
* This function stores a new value into a __weak variable. It would
* be used anywhere a __weak variable is the target of an assignment.
*
* @param location The address of the weak pointer itself
* @param newObj The new object this weak ptr should now point to
*
* @return \e newObj
*/
id
objc_storeWeak(id *location, id newObj)
{
id oldObj;
SideTable *oldTable;
SideTable *newTable;
spinlock_t *lock1;
#if SIDE_TABLE_STRIPE > 1
spinlock_t *lock2;
#endif
// Acquire locks for old and new values.
// Order by lock address to prevent lock ordering problems.
// Retry if the old value changes underneath us.
retry:
oldObj = *location;
oldTable = SideTable::tableForPointer(oldObj);
newTable = SideTable::tableForPointer(newObj);
lock1 = &newTable->slock;
#if SIDE_TABLE_STRIPE > 1
lock2 = &oldTable->slock;
if (lock1 > lock2) {
spinlock_t *temp = lock1;
lock1 = lock2;
lock2 = temp;
}
if (lock1 != lock2) spinlock_lock(lock2);
#endif
spinlock_lock(lock1);
if (*location != oldObj) {
spinlock_unlock(lock1);
#if SIDE_TABLE_STRIPE > 1
if (lock1 != lock2) spinlock_unlock(lock2);
#endif
goto retry;
}
weak_unregister_no_lock(&oldTable->weak_table, oldObj, location);
newObj = weak_register_no_lock(&newTable->weak_table, newObj, location);
// weak_register_no_lock returns nil if weak store should be rejected
// Set is-weakly-referenced bit in refcount table.
if (newObj && !newObj->isTaggedPointer()) {
newObj->setWeaklyReferenced_nolock();
}
// Do not set *location anywhere else. That would introduce a race.
*location = newObj;
spinlock_unlock(lock1);
#if SIDE_TABLE_STRIPE > 1
if (lock1 != lock2) spinlock_unlock(lock2);
#endif
return newObj;
}
- 旧对象解除注册操作 weak_unregister_no_lock
该方法主要作用是将旧对象在 weak_table 中接触 weak 指针的对应绑定。根据函数名,称之为解除注册操作。从源码中,可以知道其功能就是从 weak_table 中接触 weak 指针的绑定。而其中的遍历查询,就是针对于 weak_entry 中的多张弱引用散列表。
- 新对象添加注册操作 weak_register_no_lock
这一步与上一步相反,通过 weak_register_no_lock 函数把心的对象进行注册操作,完成与对应的弱引用表进行绑定操作。
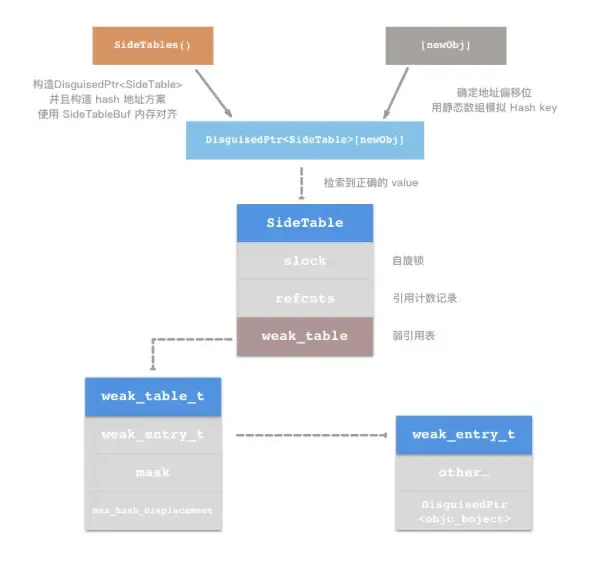
- 初始化弱引用对象流程一览 弱引用的初始化,从上文的分析中可以看出,主要的操作部分就在弱引用表的取键、查询散列、创建弱引用表等操作,可以总结出如下的流程图:

SideTable 这个结构体,是对weak_table_t表的再次封装操作,避免对weak_table_t直接操作,SideTable使用更加方便。
class SideTable {
private:
static uint8_t table_buf[SIDE_TABLE_STRIPE * SIDE_TABLE_SIZE];
public:
spinlock_t slock;
RefcountMap refcnts;
weak_table_t weak_table;
SideTable() : slock(SPINLOCK_INITIALIZER)
{
memset(&weak_table, 0, sizeof(weak_table));
}
~SideTable()
{
// never delete side_table in case other threads retain during exit
assert(0);
}
static SideTable *tableForPointer(const void *p)
{
# if SIDE_TABLE_STRIPE == 1
return (SideTable *)table_buf;
# else
uintptr_t a = (uintptr_t)p;
int index = ((a >> 4) ^ (a >> 9)) & (SIDE_TABLE_STRIPE - 1);
return (SideTable *)&table_buf[index * SIDE_TABLE_SIZE];
# endif
}
static void init() {
// use placement new instead of static ctor to avoid dtor at exit
for (int i = 0; i < SIDE_TABLE_STRIPE; i++) {
new (&table_buf[i * SIDE_TABLE_SIZE]) SideTable;
}
}
};
总之根据以上对weak进行存储的过程可以通过下边的流程图详细的描述出来
3.weak释放为nil过程 weak被释放为nil,需要对对象整个释放过程了解,如下是对象释放的整体流程:
1、调用objc_release
2、因为对象的引用计数为0,所以执行dealloc
3、在dealloc中,调用了_objc_rootDealloc函数
4、在_objc_rootDealloc中,调用了object_dispose函数
5、调用objc_destructInstance
6、最后调用objc_clear_deallocating。
对象准备释放时,调用clearDeallocating函数。clearDeallocating函数首先根据对象地址获取所有weak指针地址的数组,然后遍历这个数组把其中的数据设为nil,最后把这个entry从weak表中删除,最后清理对象的记录。
在对象被释放的流程中,需要对objc_clear_deallocating方法进行深入的分析
void objc_clear_deallocating(id obj)
{
assert(obj);
assert(!UseGC);
if (obj->isTaggedPointer()) return;
obj->clearDeallocating();
}
//执行 clearDeallocating方法
inline void objc_object::clearDeallocating()
{
sidetable_clearDeallocating();
}
// 执行sidetable_clearDeallocating,找到weak表中的value值
void objc_object::sidetable_clearDeallocating()
{
SideTable *table = SideTable::tableForPointer(this);
// clear any weak table items
// clear extra retain count and deallocating bit
// (fixme warn or abort if extra retain count == 0 ?)
spinlock_lock(&table->slock);
RefcountMap::iterator it = table->refcnts.find(this);
if (it != table->refcnts.end()) {
if (it->second & SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED) {
weak_clear_no_lock(&table->weak_table, (id)this);
}
table->refcnts.erase(it);
}
spinlock_unlock(&table->slock);
}
对weak置nil的操作最终调用执行weak_clear_no_lock方法用于执行置nil的操作。执行方法如下:
/**
* Called by dealloc; nils out all weak pointers that point to the
* provided object so that they can no longer be used.
*
* @param weak_table
* @param referent The object being deallocated.
*/
void
weak_clear_no_lock(weak_table_t *weak_table, id referent_id)
{
objc_object *referent = (objc_object *)referent_id;
weak_entry_t *entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent);
if (entry == nil) {
/// XXX shouldn't happen, but does with mismatched CF/objc
//printf("XXX no entry for clear deallocating %p\n", referent);
return;
}
// zero out references
weak_referrer_t *referrers;
size_t count;
if (entry->out_of_line) {
referrers = entry->referrers;
count = TABLE_SIZE(entry);
}
else {
referrers = entry->inline_referrers;
count = WEAK_INLINE_COUNT;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
objc_object **referrer = referrers[i];
if (referrer) {
if (*referrer == referent) {
*referrer = nil;
}
else if (*referrer) {
_objc_inform("__weak variable at %p holds %p instead of %p. "
"This is probably incorrect use of "
"objc_storeWeak() and objc_loadWeak(). "
"Break on objc_weak_error to debug.\n",
referrer, (void*)*referrer, (void*)referent);
objc_weak_error();
}
}
}
weak_entry_remove(weak_table, entry);
}
objc_clear_deallocating该函数的动作如下:
1、从weak表中获取废弃对象的地址为键值的记录
2、将包含在记录中的所有附有 weak修饰符变量的地址,赋值为nil
3、将weak表中该记录删除
4、从引用计数表中删除废弃对象的地址为键值的记录
其实Weak表是一个hash(哈希)表,然后里面的key是指向对象的地址,Value是Weak指针的地址的数组。
### 总结
是Runtime维护了一个hash(哈希)表,用于存储指向某个对象的所有weak指针。weak表其实是一个hash(哈希)表,Key是所指对象的地址,Value是weak指针的地址(这个地址的值是所指对象指针的地址)数组。